Vacuum measuring
controlling
Today, the total range of vacuum pressure accessible to measurement extends from atmospheric pressure (about 1000 mbar (750 Torr)) down to 10-12 mbar/ 0.75•10-12 Torr, i.e. it extends over 15 powers of ten. The instruments used for measuring the pressure within this wide range are called vacuum gauges. For physical reasons it is not possible to create a single vacuum sensor through which it might be possible to perform quantitative measurements within the entire pressure range. Therefore, a variety of different vacuum gauges are available, each with their own characteristic measurement range which commonly extends over several powers of ten.
Vacuum Gauges
with Mechanical Display
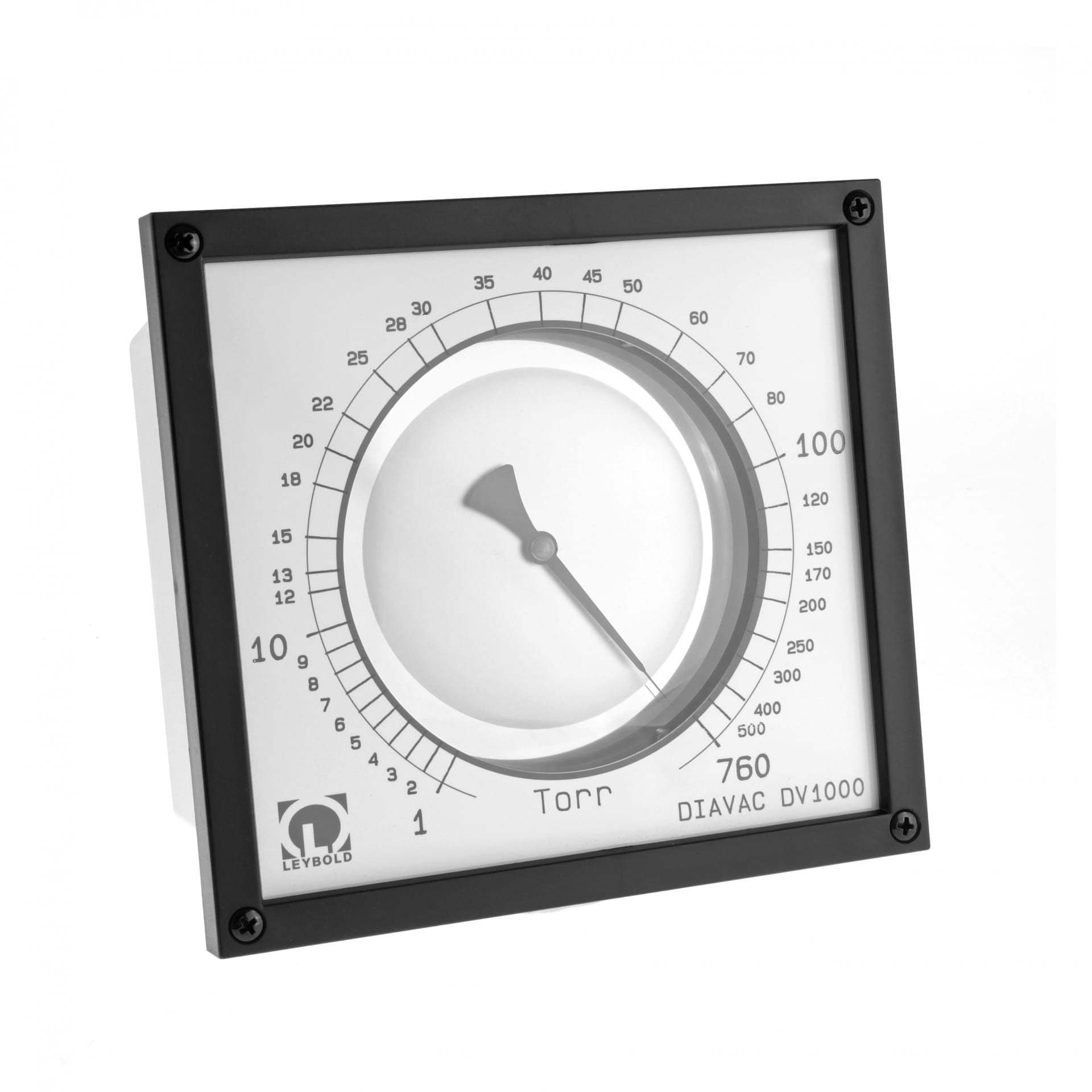
At common so-called mechanical vacuum gauges (BOURDONVAC, DIAVAC, capsule vacuum gauges) the pressure is determined directly by recording the force acting on the surface of a diaphragm. In this case of direct (or absolute) pressure measurements, the readings obtained through the vacuum gauge are independent of the type of gas and the pressure which is to be measured. The pressure range is approx. from 1000 mbar (atmospheric pressure, 750 Torr) to 1 mbar (0,75 Torr).
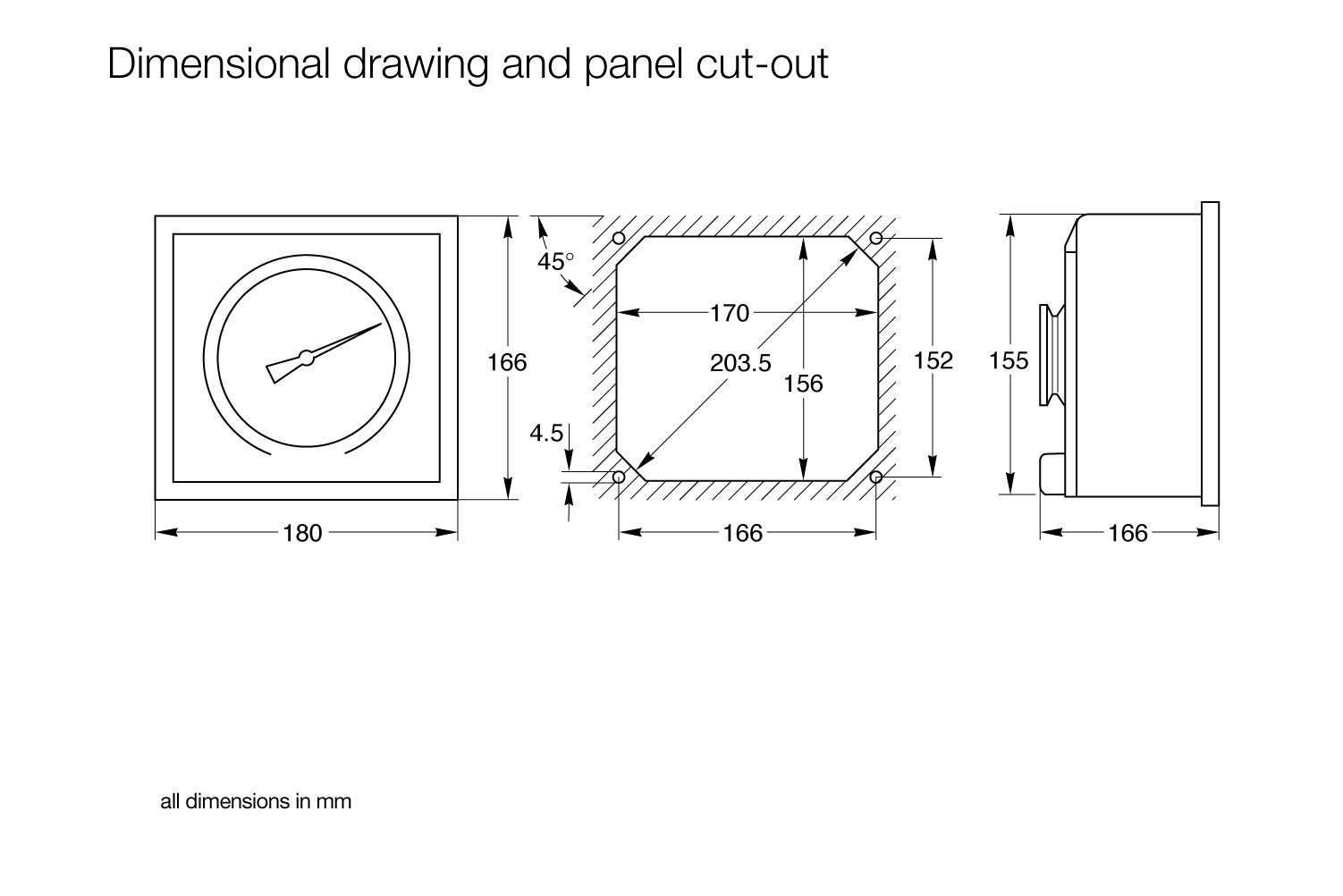
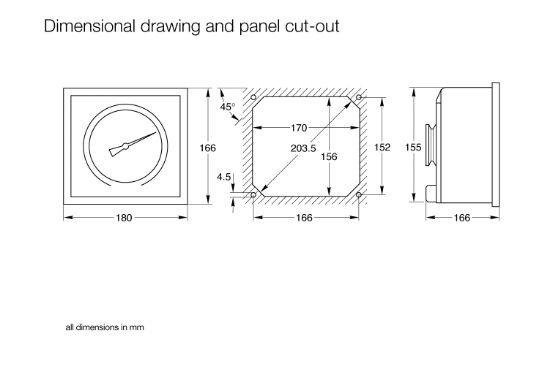
DIAVAC DV 1000